이전 게시물에선 텔레그램 봇 생성, 라즈베리파이 연결 방법에 대해 자세히 설명했다. 이번 게시물에선 프로그램의 기능을 직접 설정하고, 명령어에 코드를 연결해 프로젝트를 완성하는 과정을 소개할 것이다. 복사가 필요한 주소는 우측 상단 복사 아이콘을 클릭하면 된다! 프로젝트에 관한 게시물은 지금 게시물까지 총 3개로 마무리될 것이다.
프로젝트의 이전 게시물들은 여기에 있다.
텔레그램 API를 활용한 스마트 화분 프로젝트 – 개요, 하드웨어 구성, 회로도
텔레그램 API를 활용한 스마트 화분 프로젝트 – 텔레그램 봇 생성, 라즈베리파이 연결
🛰️ 전체 코드
코드만 필요한 독자를 위해 최종 코드를 먼저 올려두겠다. 두 번째 게시물의 모든 과정이 선행됐다는 가정 하에 만든 코드다.
전체 코드
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import logging
from grove.adc import ADC
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
from telegram import Update
from telegram.ext import Application, CommandHandler, CallbackContext
from datetime import datetime
import time
import threading
import schedule
# 텔레그램 봇의 API 키와 Chat id(-포함)를 입력하세요
TOKEN = 'YOUR_TELEGRAM_BOT_TOKEN'
GROUP_CHAT_ID = -'YOUR_GROUP_CHAT_ID'
# GPIO 핀 설정
relay_pin = 17
last_watered_file = "/home/pi/last_watered.txt"
log_file = "/home/pi/watering_log.txt"
# ADC 설정 (Grove Hat의 A0 포트를 사용)
adc = ADC()
soil_sensor_channel = 0 # A0 포트 사용
# GPIO 핀 모드 설정
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(relay_pin, GPIO.OUT)
# 로깅 설정
logging.basicConfig(
format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s',
level=logging.INFO
)
# 토양 수분 임계값 설정
SOIL_MOISTURE_THRESHOLD = 300
# 명령어 처리 함수들
def status(update: Update, context: CallbackContext) -> None:
if update.effective_chat.id != GROUP_CHAT_ID:
return
# 토양 수분 데이터를 읽어옵니다.
soil_moisture = adc.read(soil_sensor_channel)
soil_moisture_percentage = (soil_moisture / 950.0) * 100
update.message.reply_text(f"Soil moisture level: {soil_moisture_percentage:.1f}%")
# 물 주기 함수
def water(update: Update = None, context: CallbackContext = None) -> None:
if update and update.effective_chat.id != GROUP_CHAT_ID:
return
try:
# 물 주기 시작
GPIO.output(relay_pin, GPIO.HIGH)
if update:
update.message.reply_text("Watering the plant...")
time.sleep(10) # 10초 동안 물 주기 (필요시 조정)
GPIO.output(relay_pin, GPIO.LOW)
if update:
update.message.reply_text("Watering complete.")
# 현재 시간을 last_watered_file에 기록
now = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
with open(last_watered_file, "w") as f:
f.write(now)
# 물 주기 기록 로그 파일에 기록
with open(log_file, "a") as log:
log.write(f"Watered on: {now}\n")
except IOError:
if update:
update.message.reply_text("Error controlling the water pump")
# 마지막 물 준 시간 확인 함수
def lastwatered(update: Update, context: CallbackContext) -> None:
if update.effective_chat.id != GROUP_CHAT_ID:
return
try:
with open(last_watered_file, "r") as f:
last_watered_time = f.read()
update.message.reply_text(f"Last watered on: {last_watered_time}")
except FileNotFoundError:
update.message.reply_text("No record of last watering found.")
# 자동 물 주기 체크 함수
def auto_water_check():
soil_moisture = adc.read(soil_sensor_channel)
if soil_moisture < SOIL_MOISTURE_THRESHOLD:
water()
# 자동 물 주기 스케줄링 함수
def schedule_daily_check():
schedule.every().day.at("09:00").do(auto_water_check) # 매일 오전 9시에 체크
while True:
schedule.run_pending()
time.sleep(1)
# 봇 시작 함수
def main():
# Application을 생성하고, Dispatcher를 가져옵니다.
application = Application.builder().token(TOKEN).build()
# 핸들러들 등록
application.add_handler(CommandHandler("status", status))
application.add_handler(CommandHandler("water", water))
application.add_handler(CommandHandler("lastwatered", lastwatered))
# 자동 물 주기 체크 스레드 시작
threading.Thread(target=schedule_daily_check, daemon=True).start()
# 봇 시작
application.run_polling()
# 메인 함수 실행
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()GPIO 핀과 ADC 설정은 개인 회로도에 맞게 커스텀하면 되고, 임계값은 센서의 측정 범위에 따라 적절한 값을 적어주면 되므로 설명을 생략하겠다.
🧩 각 명령어 설정 및 코드
명령어는 텔레그램 봇을 통해 ‘status’ , ‘water’ , ‘lastwatered’로 총 3개 만들었지만, 사용자가 직접 제어하지 않아도 되는 자동화 함수인 ‘schedule_daily_check’도 추가됐다.
그룹챗에서 ‘status’ 명령어가 입력되면,
def status(update: Update, context: CallbackContext) -> None:
if update.effective_chat.id != GROUP_CHAT_ID:
return
# 토양 수분 데이터를 읽어옵니다.
soil_moisture = adc.read(soil_sensor_channel)
# 센서값을 백분율로 변환해 출력합니다. (950에 해당하는 값 = 센서의 최대 측정값)
soil_moisture_percentage = (soil_moisture / 950.0) * 100
update.message.reply_text(f"Soil moisture level: {soil_moisture_percentage:.1f}%")- 토양 수분 데이터를 읽는다
- 센서값을 백분율로 변환해 출력한다.
두 과정을 거친다. 내가 사용한 센서는 0-950까지의 값이 측정돼서 사용자가 직관으로 토양습도를 인식하기 쉽지 않다는 판단이 들어 2번 과정을 추가했다.
‘water’ 명령어가 입력되면,
def water(update: Update = None, context: CallbackContext = None) -> None:
if update and update.effective_chat.id != GROUP_CHAT_ID:
return
try:
# 물 주기 시작
GPIO.output(relay_pin, GPIO.HIGH)
if update:
update.message.reply_text("Watering the plant...")
time.sleep(10) # 10초 동안 물 주기 (필요시 조정)
GPIO.output(relay_pin, GPIO.LOW)
if update:
update.message.reply_text("Watering complete.")
# 현재 시간을 last_watered_file에 기록
now = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
with open(last_watered_file, "w") as f:
f.write(now)
# 물 주기 기록 로그 파일에 기록
with open(log_file, "a") as log:
log.write(f"Watered on: {now}\n")
except IOError:
if update:
update.message.reply_text("Error controlling the water pump")- 물 주기를 시작하고, 물을 주고 있다는 메시지를 그룹챗에 보낸다.
- 10초간 물을 준다
- 물 주기가 끝나면, 물을 다 줬다는 메시지를 그룹챗에 보낸다.
- 현재 시간을 ‘last_watered_file’와 로그 파일에 기록한다.
‘last watered’ 명령어가 입력되면,
def lastwatered(update: Update, context: CallbackContext) -> None:
if update.effective_chat.id != GROUP_CHAT_ID:
return
try:
with open(last_watered_file, "r") as f:
last_watered_time = f.read()
update.message.reply_text(f"Last watered on: {last_watered_time}")
except FileNotFoundError:
update.message.reply_text("No record of last watering found.")- ‘last_watered_file’을 열어 마지막으로 물을 준 시간을 확인한다.
- 기록된 시간 혹은 기록이 없다는 에러 메시지를 그룹챗에 보낸다.
그리고, 자동화 함수인 ‘schedule_daily_check’는
# 자동 물 주기 체크 함수
def auto_water_check():
soil_moisture = adc.read(soil_sensor_channel)
if soil_moisture < SOIL_MOISTURE_THRESHOLD:
water()
# 자동 물 주기 스케줄링 함수
def schedule_daily_check():
schedule.every().day.at("09:00").do(auto_water_check) # 매일 오전 9시에 체크
while True:
schedule.run_pending()
time.sleep(1)- 매일 아침 9시에 토양 수분의 값을 측정한다.
- 센서값이 초기에 설정한 임계값보다 낮으면, water 함수를 실행한다.
🍾 핸들러 등록 및 실행
# 봇 시작 함수
def main():
# Application을 생성하고, Dispatcher를 가져옵니다.
application = Application.builder().token(TOKEN).build()
# 핸들러들 등록
application.add_handler(CommandHandler("status", status))
application.add_handler(CommandHandler("water", water))
application.add_handler(CommandHandler("lastwatered", lastwatered))
# 자동 물 주기 체크 스레드 시작
threading.Thread(target=schedule_daily_check, daemon=True).start()
# 봇 시작
application.run_polling()
# 메인 함수 실행
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()이렇게 완성된 코드를 실행하면, 그룹챗에는 이런 화면이 뜬다.
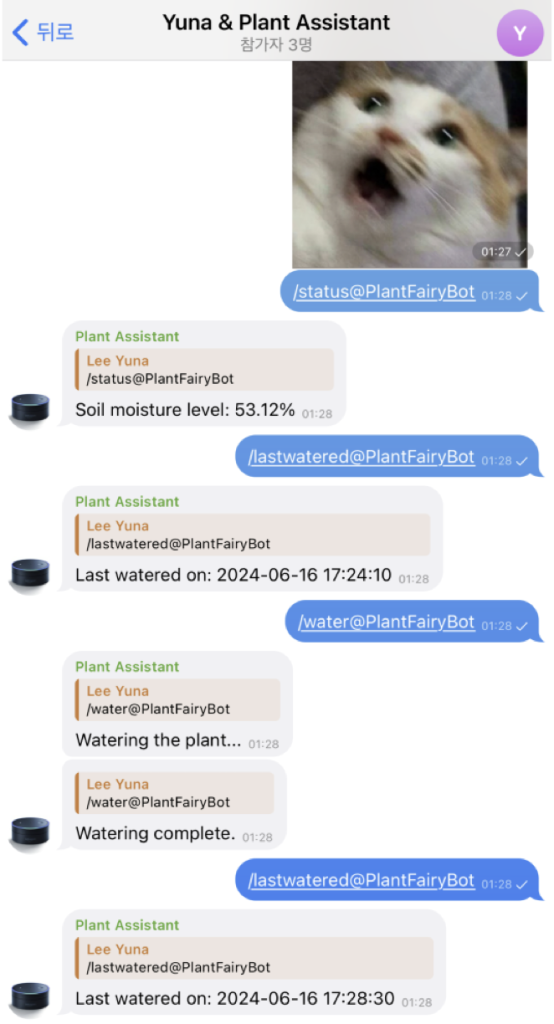
실제 실행환경은 이렇다.
🪗 프로젝트 마무리 소감
아무래도 마감이 정해져 있는 파이널 프로젝트다 보니 디테일한 부분에 신경을 못 쓴 것 같아 아쉬움이 남는다. 그래도 혼자 처음부터 끝까지 진행했고, 라즈베리파이는 물론이고 쉘 개발 환경도 다 처음이었던 백그라운드에 비하면 아주 훌륭한 마무리였다고 생각한다. 하하. 내가 좋아하는 메신저인 텔레그램을 사용해 진행해서 더 애정이 갔던 프로젝트였다. 추후에 텔레그램의 확장성에 대해 더 깊게 고민하고 철저히 준비해서 좀 더 규모 있는 프로젝트를 진행해보고 싶다.
![[KakaoTech] 이론기간 회고 | 기술에 대한 명확한 이해와 반복숙달](https://icecreamzoa.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/image-6.png)

답글 남기기